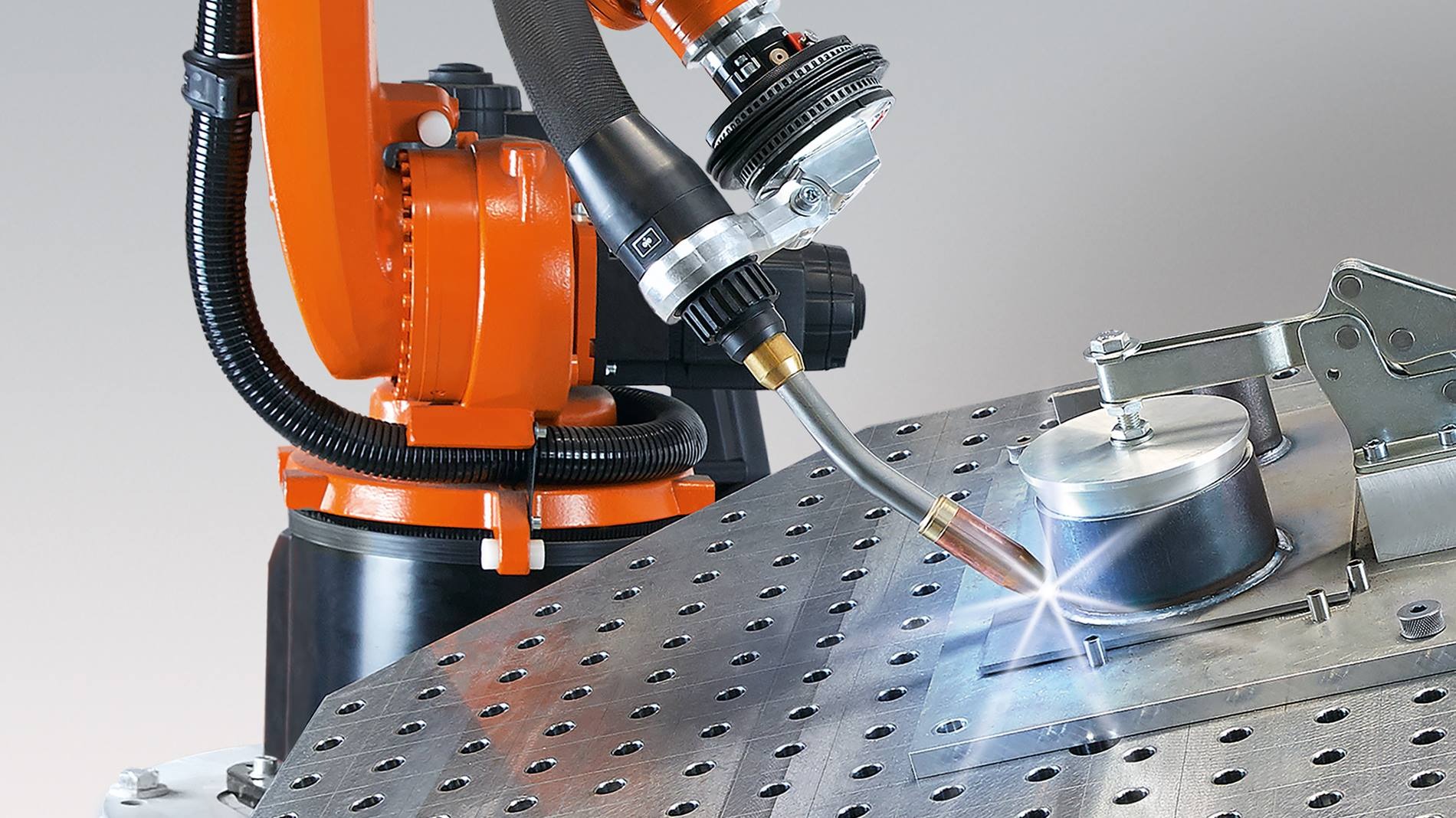
As industries strive for faster production and higher precision, the integration of robotics into traditional processes has become a game-changer. Welding, a cornerstone of manufacturing and fabrication, is now being revolutionised by the use of robotic systems. The fusion of robots and welding is not just a trend—it’s a leap forward in industrial efficiency and capability.
Manufacturers across the globe are under pressure to meet rising demands while navigating labour shortages and quality control. Robotic welding delivers both speed and accuracy, making it a key driver of smart manufacturing strategies.
Key Points:
- Robotic welding enhances both speed and precision in production.
- Automated systems reduce human exposure to harmful environments.
- Robots offer consistency and eliminate variability in weld quality.
- Labour shortages are offset by robotic integration and reallocation of human roles.
- Robotic welders can adapt quickly to design changes and product variation.
The Shift Towards Robotic Welding
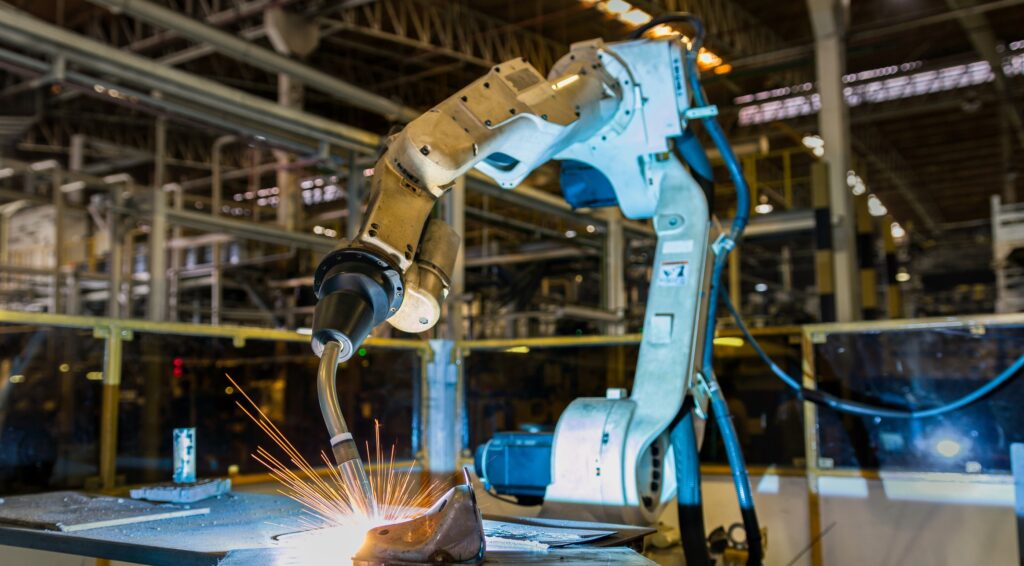

Welding has always required a skilled hand, but robotic welding systems have changed the game by introducing unmatched levels of consistency and control. These systems are designed to carry out programmed welding operations automatically, combining mechanical dexterity with software intelligence.
Robots can handle repetitive welding tasks with pinpoint accuracy, operating around the clock without fatigue. Their precision helps reduce material waste and welding defects, making them invaluable in industries where quality and speed are paramount—such as automotive manufacturing, heavy engineering, and shipbuilding.
Why Manufacturers Are Making the Switch
The adoption of robotic welding is accelerating, driven by several compelling advantages:fss of the shift or workload.
- Productivity Boost: Robotic systems work continuously, drastically reducing cycle times and increasing output.
- Health and Safety Improvements: By handling dangerous tasks, robots keep human workers safer and reduce exposure to harmful fumes and intense light.
- Labour Optimisation: With skills shortages affecting many sectors, robots fill critical gaps and allow human operators to focus on oversight and quality assurance.
Customisation and Flexibility
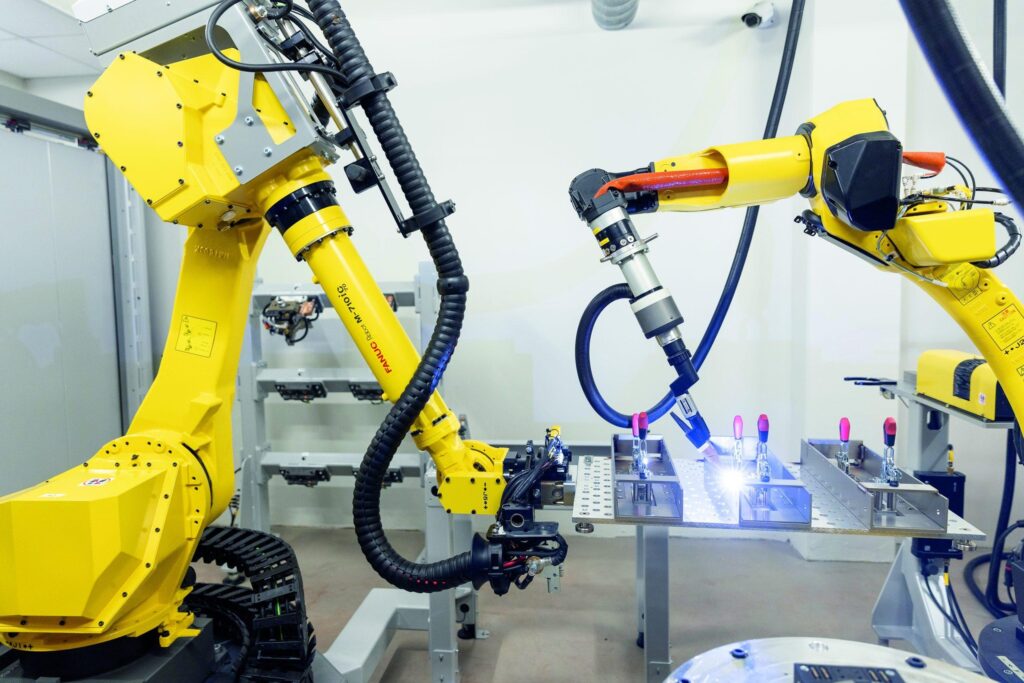

One of the greatest strengths of robotic welding systems is their adaptability. Today’s solutions can be customised to fit a wide range of applications, from mass production to low-volume, high-variation manufacturing. Modern robots can be reprogrammed with ease, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in design or production demand.
Companies looking to integrate robotic welding should consider both the technical aspects and the strategic benefits. Selecting the right automation partner can make all the difference in terms of performance and return on investment.
To explore how robots and welding can benefit your operations, Cyber-Weld provides expert support and integration services tailored to your manufacturing needs.
Choosing the Right Application Strategy
Before adopting robotic welding, manufacturers should assess where automation fits best. Not all tasks benefit equally from robotic execution. Short-run or highly customised jobs might still require human welders. The real value comes from automating predictable, repeatable operations.
Recommendations for identifying the right fit:
- Evaluate Repetition: High-volume tasks are ideal candidates.
- Measure Complexity: Simpler weld paths translate to faster automation payback.
- Factor in Risk: Dangerous processes should be automated first.
- Check Existing Skill Gaps: Automation fills roles you can’t easily hire for.
- Forecast Design Changes: Choose flexible systems for variable production lines.
A careful assessment prevents overinvestment and ensures automation serves strategic goals.
Training Human Workers for Robotic Oversight
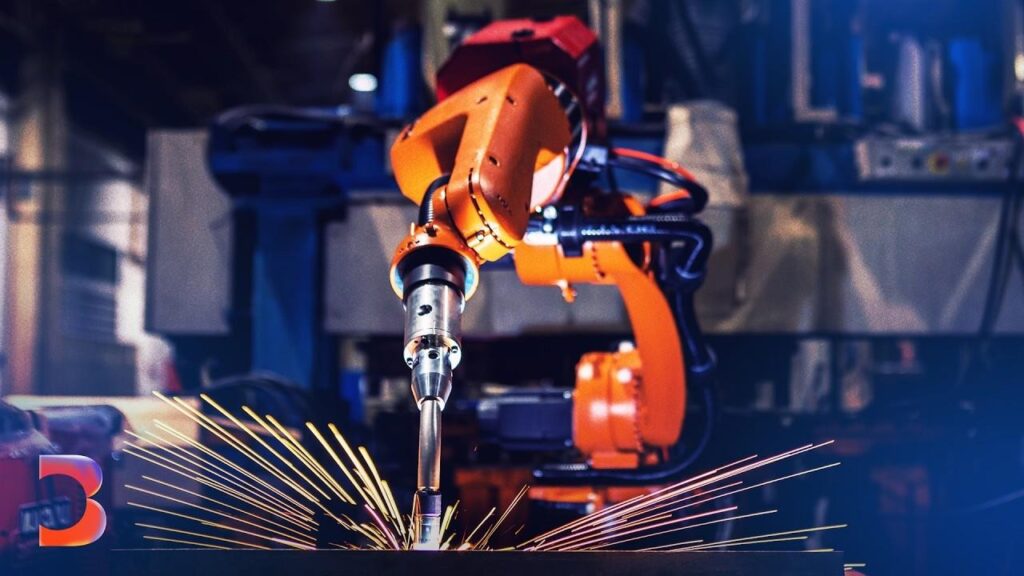

As robots take on more welding tasks, human roles don’t disappear—they shift. Instead of manual welders, companies now need technicians and supervisors who can manage robotic systems, troubleshoot issues, and fine-tune processes.
Key skills for workforce transition:
- Operating and programming robotic arms.
- Understanding welding parameters and how robots apply them.
- Diagnosing faults or system downtime quickly.
- Coordinating between quality assurance and production output.
Retraining programs and vocational courses help prepare staff. Investing in employee growth supports long-term success and technology retention.
Common Missteps to Avoid When Automating Welding
Automation brings big gains, but poor planning can cost more than it saves. Companies often overlook the full scope of integration or underestimate what’s needed to maintain systems.
Top mistakes to avoid:
- Ignoring Workspace Layout: Robots need clear paths and access points.
- Choosing Oversized Equipment: Bigger isn’t always better. Select based on need.
- Skipping Simulation Tests: Virtual modelling catches layout or timing issues early.
- Underestimating Maintenance: Regular checks keep the system running smoothly.
- Neglecting Operator Training: Human oversight still plays a critical role.
Success in robotic welding isn’t just about hardware—it’s about precision in planning, support, and operation.
Economic Impact of Robotic Welding
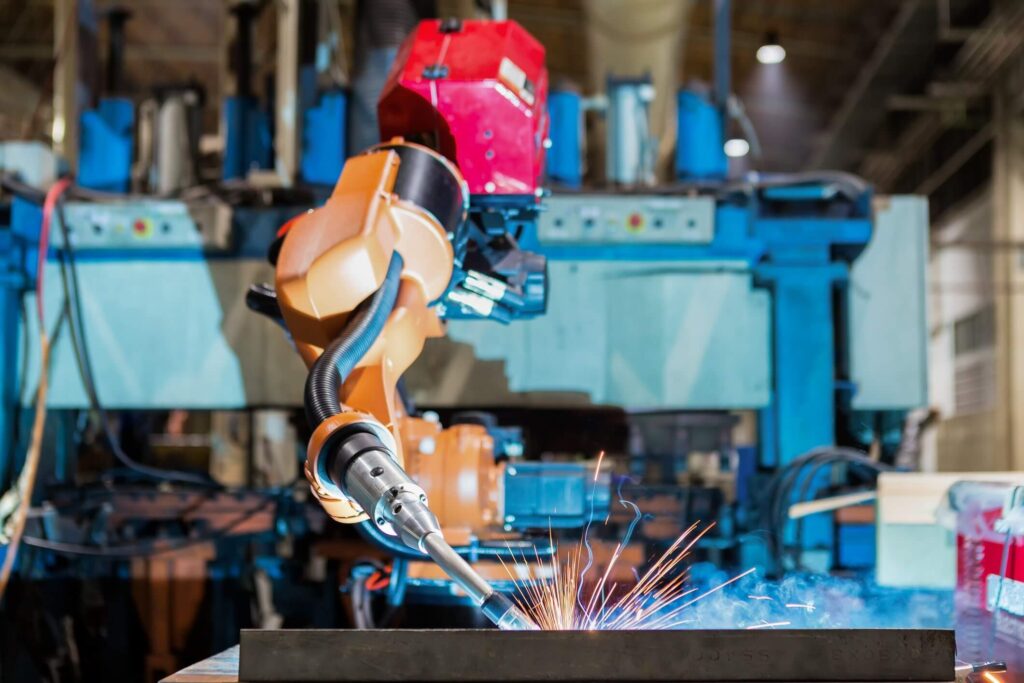

The return on investment in robotic welding is not limited to productivity alone. Companies gain long-term financial stability by reducing errors, lowering rework costs, and improving resource allocation.
A robot can complete hundreds of welds with consistent accuracy, cutting down the scrap rate significantly. Less material waste directly reduces operating costs. Insurance premiums may drop due to improved worker safety. Reduced downtime adds even more value.
Mid-sized manufacturers often see ROI within two to three years. Larger operations reach break-even faster. With accurate forecasting and smart implementation, the financial case for robotic welding stands on solid ground.
Looking Ahead
With rapid advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and control systems, the future of welding will only become more autonomous and intelligent. Robotic welders will increasingly take on more complex tasks, guided by real-time data and adaptive algorithms.
For manufacturers aiming to stay ahead in a competitive market, adopting robotic welding is not just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic move towards operational excellence.